ECHA has released proposals to identify eight chemical substances as Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC). Substances that may have serious and often irreversible effects on human health and the environment can be identified as SVHCs. If a substance is identified as an SVHC, it will be added to the Candidate List of REACH for eventual inclusion in the Authorisation List. Currently there are 211 substances on the SVHC Candidate List.
The proposed substances and examples of their use are:
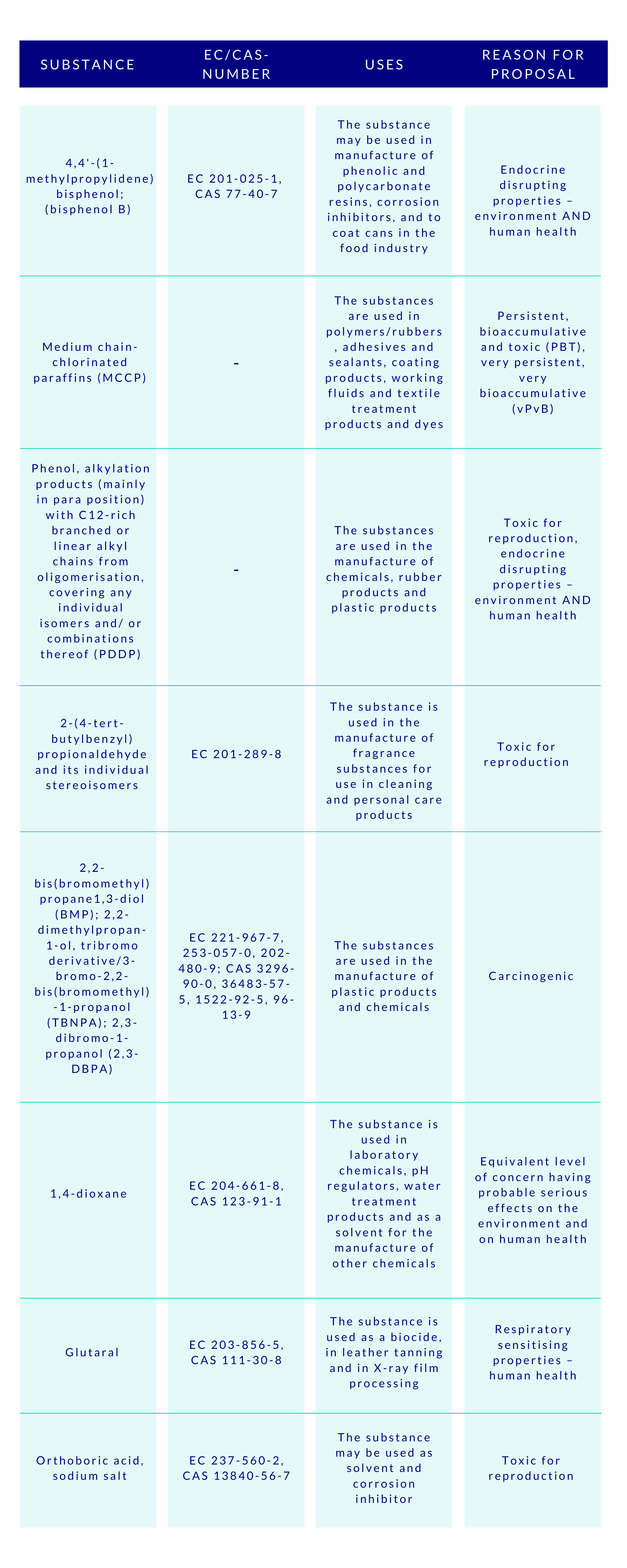
More information about the substances and links to comment are found at the ECHA website. The deadline for comments is 23 April 2021. Comments received on uses, and volumes per use, exposure, alternatives and risks will be taken into account in the authorisation process. Proposal and comments are referred to the Member State Committee (MSC) for agreement. If the committee does not reach a unanimous agreement, the matter is referred to the European Commission for a final decision. The substance is included directly in the Candidate List if no comments challenging the identification are received.
Obligations related to SVHC
Companies have legal obligations if a substance included in the Candidate List is present in a concentration above 0.1% w/w. Obligations include:
- Providing Safety Data Sheets for substances on their own and substances in mixtures containing SVHCs
- Requirement to notify ECHA under REACH if an article contains a SVHC
- Requirement to inform customers and consumers under REACH if an article contains a SVHC to allow safe use of the article
- Requirement to notify ECHA under the Waste Framework Directive (SCIP Database) about articles containing SVHCs
Companies that are importing, producing, selling or using substances, their mixtures or articles (components, materials) containing SVHCs should keep an eye on the substances added to the Candidate List. Substances are regularly being added to the list. It is also recommended for companies to start looking for substitutes for the added substances already. Substances on the Candidate List may also be placed on the Authorisation List in the future, which means that continuing the use would need a permission.
Do you need help with chemical management?
Our experienced chemical consultants will assist you in meeting your chemical requirements. Furthermore, our Ecobio Manager SaaS-service will help you manage your chemicals and ensure compliance with global regulations. Interested? Contact us today!
Contact: info@ecobio.fi
Text: Mikael Hirn
Picture: Shutterstock
Sources:
ECHA Weekly – 10 March 2021.










